Planar Gaussian Splatting (WACV 2024)
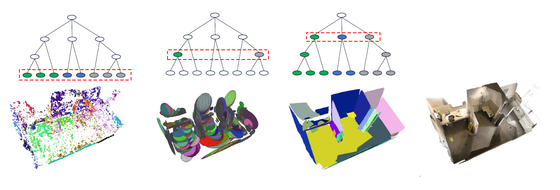
Planar Gaussian Splatting (PGS) introduces a novel neural rendering approach to learn the 3D geometry and parse the 3D planes of a scene, directly from multiple RGB images. The PGS leverages Gaussian primitives to model the scene and employ a hierarchical Gaussian mixture approach to group them. Similar Gaussians are progressively merged probabilistically in the tree-structured Gaussian mixtures to identify distinct 3D plane instances and form the overall 3D scene geometry.
The PGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D planar reconstruction without requiring either 3D plane labels or depth supervision. In contrast to existing supervised methods that have limited generalizability and struggle under domain shift, PGS maintains its performance across datasets thanks to its neural rendering and scene-specific optimization mechanism.
Neural Mesh Fusion: UNSUPERVISED 3D PLANAR SURFACE UNDERSTANDING (IEEE ICIP 2024)
Neural Mesh Fusion (NMF) is a method for joint optimization of polygon meshes, estimated from multi-view image observations and unsupervised 3D planar-surface parsing of the scene. In contrast to implicit neural representations, NMF directly learns to deform surface triangle mesh and generate an embedding for unsupervised 3D planar segmentation through gradient-based optimization directly on the surface mesh. The conducted experiments show that NMF obtains competitive results compared to state-of-the-art multi-view planar reconstruction, while not requiring any ground-truth 3D or planar supervision.
- Arxiv version (link)
VaLID: Variable-Length Input Diffusion for Novel View Synthesis (WACV 2024)
VaLID is a deep generative AI model. It performs novel-view image synthesis by processing either a single input image or variable-length multi-view images. This highly adaptive property of VaLID enables various applications in 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis.
- Arxiv version (link)
Deep Learning Frameworks for Weakly-supervised Indoor Wi-Fi Positioning (2020-2021)
Deep learning solutions for the large-scale indoor localization of people and robot agents via Wi-Fi signal with accessing only to a few room/zone level annotations.
- NeurIPS demo, 2021 (link)
- Video on youtube (link)
Corresponding manuscripts:
- Modality-agnostic topology aware localization (link)
Farhad G. Zanjani, Ilia Karmanov, Hanno Achermann, Daniel Dijkman, Simone Merlin, Max Welling, Fatih Porikli.
NeurIPS, 2021.
- WiCluster: Passive Indoor 2D/3D Positioning using WiFi without Precise Labels (link)
Ilia Karmanov, Farhad G. Zanjani, Simone Merlin, Ishaque Kadampot, Daniel Dijkman
IEEE Globecom, 2021.
- Deep Learning Frameworks for Weakly-Supervised Indoor Localization (link)
Farhad G. Zanjani, Ilia Karmanov et al., NeurIPS Competitions and Demonstrations Track, 2021.
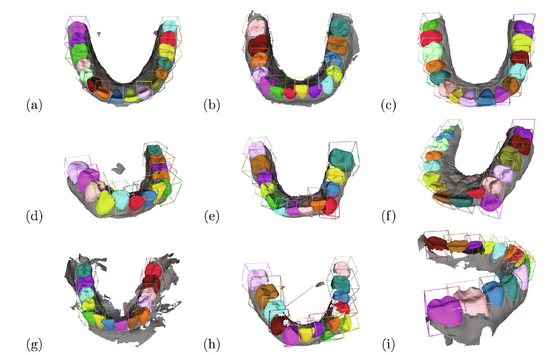
- Mask-MCNet: Tooth instance segmentation in 3D point clouds of intra-oral scans. Neurocomputing Journal, 2021 (link).
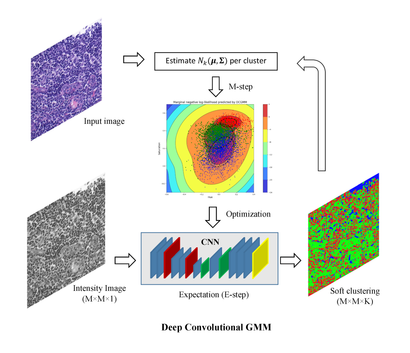
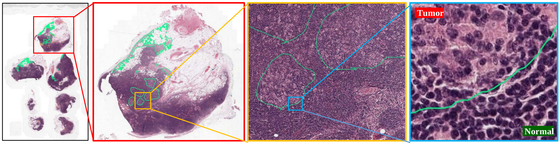
- Deep convolutional gaussian mixture model for stain-color normalization or histopathological images; Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI),
2018.

- Histopathology stain-color normalization using deep generative models,Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (MIDL), 2018.

- Stain normalization of histopathology images using generative adversarial networks; IEEE Int. Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2018.

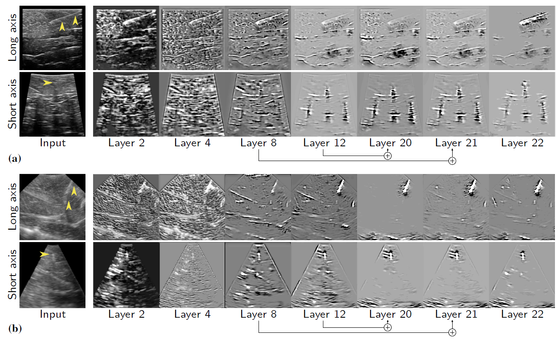
- Robust and semantic needle detection in 3D ultrasound using orthogonal-plane convolutional neural networks;International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery,
2018.

- Improving needle detection in 3D ultrasound using orthogonal-plane convolutional networks;Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention
(MICCAI), 2017.

- Coherent needle detection in ultrasound volumes using 3D conditional random fields;Proc.or SPIE Medical Imaging, 2018.

- Localization of partially visible needles in 3D ultrasound using dilated CNNs; IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), 2019